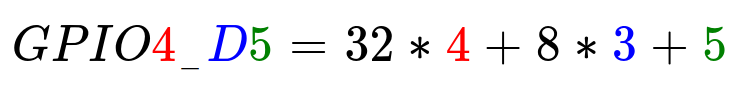Difference between revisions of "Rockpi4/hardware/gpio"
(→ROCK Pi 4C Plus general purpose input-output (GPIO) connector) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<div class="panel-heading"><h3>Hardware</h3></div> | <div class="panel-heading"><h3>Hardware</h3></div> | ||
<div class="panel-body"> | <div class="panel-body"> | ||
| − | === <span id="gpio">'''Rock Pi | + | === <span id="gpio">'''Rock Pi 4A / 4A Plus / 4B / 4B Plus / 4C / 4C Plus(>=V1.2)''' general purpose input-output (GPIO) connector</span> === |
ROCK Pi 4 has a 40-pin expansion header. Each pin is distinguished by color. | ROCK Pi 4 has a 40-pin expansion header. Each pin is distinguished by color. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === <span id="rockpi4c+gpio">'''ROCK Pi 4C Plus''' general purpose input-output (GPIO) connector</span> === | + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="overflow:auto;"> |
| + | |||
| + | === <span id="rockpi4c+gpio">'''ROCK Pi 4C Plus V1.0/V1.1''' general purpose input-output (GPIO) connector</span> === | ||
ROCK Pi 4C Plus has a 40-pin expansion header. Each pin is distinguished by color. | ROCK Pi 4C Plus has a 40-pin expansion header. Each pin is distinguished by color. | ||
| Line 113: | Line 115: | ||
* For I2C-2 and I2C-7 | * For I2C-2 and I2C-7 | ||
** We have do the test using the i2c device e2prom. We need to open the i2c device file, and then do the read or write operation. | ** We have do the test using the i2c device e2prom. We need to open the i2c device file, and then do the read or write operation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
=== IO Voltage === | === IO Voltage === | ||
Revision as of 02:25, 11 May 2022
ROCK Pi 4 > Hardware > GPIO
Contents
[hide]Hardware
Rock Pi 4A / 4A Plus / 4B / 4B Plus / 4C / 4C Plus(>=V1.2) general purpose input-output (GPIO) connector
ROCK Pi 4 has a 40-pin expansion header. Each pin is distinguished by color.
| GPIO number | Function2 | Function1 | GPIO | Pin# | Pin# | GPIO | Function1 | Function2 | GPIO number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +3.3V | 1 | 2 | +5.0V | |||||||
| 71 | I2C7_SDA | GPIO2_A7 | 3 | 4 | +5.0V | |||||
| 72 | I2C7_SCL | GPIO2_B0 | 5 | 6 | GND | |||||
| 75 | SPI2_CLK | GPIO2_B3 | 7 | 8 | GPIO4_C4 | UART2_TXD | 148 | |||
| GND | 9 | 10 | GPIO4_C3 | UART2_RXD | 147 | |||||
| 146 | PWM0 | GPIO4_C2 | 11 | 12 | GPIO4_A3 | I2S1_SCLK | 131 | |||
| 150 | PWM1 | GPIO4_C6 | 13 | 14 | GND | |||||
| 149 | SPDIF_TX | GPIO4_C5 | 15 | 16 | GPIO4_D2 | 154 | ||||
| +3.3V | 17 | 18 | GPIO4_D4 | 156 | ||||||
| 40 | UART4_TXD | SPI1_TXD | GPIO1_B0 | 19 | 20 | GND | ||||
| 39 | UART4_RXD | SPI1_RXD | GPIO1_A7 | 21 | 22 | GPIO4_D5 | 157 | |||
| 41 | SPI1_CLK | GPIO1_B1 | 23 | 24 | GPIO1_B2 | SPI1_CSn | 42 | |||
| GND | 25 | 26 | ADC_IN0 | |||||||
| 64 | I2C2_SDA | GPIO2_A0 | 27 | 28 | GPIO2_A1 | I2C2_CLK | 65 | |||
| 74 | I2C6_SCL | SPI2_TXD | GPIO2_B2 | 29 | 30 | GND | ||||
| 73 | I2C6_SDA | SPI2_RXD | GPIO2_B1 | 31 | 32 | GPIO3_C0 | SPDIF_TX | UART3_CTSn | 112 | |
| 76 | SPI2_CSn | GPIO2_B4 | 33 | 34 | GND | |||||
| 133 | I2S1_LRCK_TX | GPIO4_A5 | 35 | 36 | GPIO4_A4 | I2S1_LRCK_RX | 132 | |||
| 158 | GPIO4_D6 | 37 | 38 | GPIO4_A6 | I2S1_SDI | 134 | ||||
| GND | 39 | 40 | GPIO4_A7 | I2S1_SDO | 135 |
[Expand]
IO Voltage
RK3399 have three IO voltages, 1.8V/3.0V/3.3V. For ROCK Pi 4, below is the default voltage:
| GPIO | Voltage Level | Tolerance | | ---------- | ------------- | --------- | | GPIO3_C0 | 3.3V | 3.465V | | ADC_IN0 | 1.8V | 1.98V | | Other GPIO | 3.0V | 3.14V |
GPIO number
Rockchip RK3399 GPIO has 5 banks, GPIO0 to GPIO4, each bank has 32pins, naming as below:
GPIO0_A0 ~ A7 GPIO0_B0 ~ B7 GPIO0_C0 ~ C7 GPIO0_D0 ~ D7 GPIO1_A0 ~ A7 .... GPIO1_D0 ~ D7
For Rockchip 4.4 kernel, the GPIO number can be calculated as below, take GPIO4_D5 (PIN22 on 40PIN GPIO) as an example:
GPIO4_D5 = 4*32 + 3*8 + 5 = 157 (A=0, B=1, C=2, D=3)
To set GPIO4_D5 output
cd /sys/class/gpio echo 157 > export cd gpio157 echo out > direction echo 1 > value # output high echo 0 > value # output low