Difference between revisions of "RockpiS/getting started"
(→Close look of ROCK Pi S) |
|||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Languages|rockpiS/getting_started}} | {{Languages|rockpiS/getting_started}} | ||
| + | [[rockpiS | ROCK Pi S]] > [[rockpiS/getting_started | Getting started]] | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
** μSD card, larger than 8GB. | ** μSD card, larger than 8GB. | ||
| − | * | + | * USB type C to type A cable |
| − | + | ** For both power and USB communication(adb/fastboot) with HOST PC. | |
| − | ** | + | |
| − | * USB | + | * PC/Laptop which has USB ports |
| − | ** | + | ** The ROCK Pi S can be powered from the PC/Laptop USB ports directly |
=== Optional === | === Optional === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Power adapter | ||
| + | ** If you want to power ROCK Pi S standalone, you can use 5V/1A or 5V/2A power adapter with USB C ports. You can also use the USB PD/QC power adapter without worrying damage the board because the PD/QC adapter will detect ROCK Pi S only supports 5V so the adapter will output 5V. | ||
| + | |||
* μSD Card Reader | * μSD Card Reader | ||
| − | ** For flashing the image into μSD Card | + | ** For flashing the image into μSD Card. |
| − | * USB | + | * USB to TTL serial cable |
| − | ** | + | ** For serial console, low level troubleshooting, development etc. |
* Ethernet cable | * Ethernet cable | ||
| Line 48: | Line 52: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Processor | ! Processor | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | - | + | | colspan="2" | SoC RK3308B <br />Quad Cortex-A35 ARM 64bits processor <br /> frequency up to 1.0GHz |
|- | |- | ||
! Memory | ! Memory | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | 256MB or 512MB DDR3 |
|- | |- | ||
! Storage | ! Storage | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | MicroSD(TF), optional on board 1/2/4/8Gb NAND flash |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Wireless | ! Wireless | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | 802.11 b/g/n wifi <br /> BT 4.0(rtl8723DS) <br /> external antenna |
|- | |- | ||
! USB | ! USB | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | --- | + | | colspan="2" | USB2.0 Type-A HOST x1 <br /> USB3.0 Type-C OTG x1 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | !| Key | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | maskrom x1 <br /> reset x1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Ethernet | ! Ethernet | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | 100MB ethernet, optional PoE(additional HAT requried) |
|- | |- | ||
! IO | ! IO | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | - | + | | colspan="2" | 26-pin expansion header <br /> I2C x4 <br /> PWM x3 <br /> SPI x2<br /> UART x3<br /> I2S0 x1<br /> 5V DC power in x2 <br /> 3.3V DC power in x2 |
|- | |- | ||
! Others | ! Others | ||
| Line 75: | Line 79: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Power | ! Power | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | - | + | | colspan="2" | USB Type-C DC 5V |
|- | |- | ||
! Size | ! Size | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | 1.7inch square |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 87: | Line 91: | ||
ROCK Pi S can be started with μSD Card. | ROCK Pi S can be started with μSD Card. | ||
| − | === Prepare === | + | === 1. Prepare the image === |
* When start system with μSD Card | * When start system with μSD Card | ||
Insert the μSD Card into μSD Card Reader, which connects to host computer. | Insert the μSD Card into μSD Card Reader, which connects to host computer. | ||
| − | === Write Image === | + | === 2. Write Image to uSD card === |
* Download the flash tool, etcher, from [[rockpiS/downloads | Downloads]]. Choose the right version for your host operation system. Here we operate on host Ubuntu 16.04. | * Download the flash tool, etcher, from [[rockpiS/downloads | Downloads]]. Choose the right version for your host operation system. Here we operate on host Ubuntu 16.04. | ||
| Line 118: | Line 122: | ||
[[File:linux_etcher_show_complete.png]] | [[File:linux_etcher_show_complete.png]] | ||
| − | === Boot === | + | === 3. Boot the board === |
| + | |||
| + | * Now insert the uSD card to the board. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Use a USB C to USB A cable, connect the board to your PC | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ROCK Pi S will boot, the green power led is on, and after a while, the blue led start blinking | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (Optional)Use a USB to TTL serial cable to make a connection between your PC and ROCK Pi S. See [[rockpiS/dev/serial-console | Serial Console]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 4. Access from the Host PC/Laptop === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Option 1: USB access(adb) ==== | ||
| + | By default, the ROCK Pi S Linux image enables adbd services, which is a debug bridge from Android now ported on Linux. With one USB A to C cable you can power and access the board, very handy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To use adb, you need to install adb tool on the PC/Laptop. Check instructions for [[Rock/windows_adb | Windows]] and [[Rock/linux_adb | Linux]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After you have adb installed successfully, run the following command on console to login the shell of ROCK Pi S: | ||
| + | |||
| + | adb shell | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check [[rockpiS/dev/adb | Using adb]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Option 2: Serial console ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check [[rockpiS/dev/serial-console | Serial Console]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Option 3: SSH ==== | ||
| + | SSH server is enabled on port 22 of ROCK Pi S default image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Please use [https://angryip.org/ angryip] to find your board IP address. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To access ROCK Pi S by SSH, try | ||
| + | |||
| + | ping rockpis.local | ||
| + | ssh rock@rockpis.local | ||
| + | |||
| + | or if your router/network doesn't support Local Domain, you need to check your network/router administrator page and look for the ROCK Pi S ip address. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ping ip-of-device | ||
| + | ssh rock@ip-of-device | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: You can also get the IP of ROCK Pi S from option 1 or option 2 if you can not access network administrator page. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 5.Network state === | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Look at network configure: | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ sudo ifconfig | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Test network: | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ ping -c 5 www.google.com | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 6.WIFI Connection === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check [[rockpiS/Debian#WIFI Connection| WIFI Connection]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 7.BT === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check [[rockpiS/Debian#BT| BT]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 8.Buttons === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ROCK Pi S has reset key and maskrom key: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Keys.jpeg | 300px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reset key: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Press and release this key to reset ROCK Pi S. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Maskrom key: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ROCK Pi S supports boot on SD NAND flash. By default, SD NAND starts before TF card. Press the maskrom key to ignore the SD NAND flash when ROCK Pi S is powered on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 9.LED === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ROCK Pi S has Power LED and User LED. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Power LED | ||
| + | |||
| + | Power LED is green, which can be configured by sysfs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The related directory is /sys/class/leds/rockpis:green:power | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is always on when ROCK Pi S is given power by default, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * User LED | ||
| + | |||
| + | User LED is blue, which can be configured by sysfs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The related directory is /sys/class/leds/rockpis:blue:user | ||
| + | |||
| + | By default, its blink status shows the running kernel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 10.GPIO === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ROCK Pi S has two 26-pin expansion headers. Each pin is distinguished by color, more information click [https://wiki.radxa.com/RockpiS/hardware/gpio here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Development for GPIO ROCK Pi S support libmraa GPIO library, click [https://wiki.radxa.com/RockpiS/dev/libmraa here] to get more information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 11.Using OTG === | ||
| − | + | ROCK Pi S has an USB type-C OTG connector, which you can use to write(or read) data by PC to (or from) ROCK Pi S, more help click [https://wiki.radxa.com/RockpiS/dev/otg here] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Next Step == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * [[RockpiS/Debian | More Debian image usage and tips]] | |
| + | * [[RockpiS/dev/sdnand-install | Install image to SD Nand if your board has]] | ||
| + | * [[RockpiS/hardware | Checkout the hardware details]] | ||
| + | * Join the [https://forum.radxa.com/c/rockpiS community] and the [https://t.me/rockpi4 discussion group] | ||
| − | + | == Troubleshooting == | |
* Refer [[RockpiS/getting_started/troubleshooting | Troubleshooting page]] | * Refer [[RockpiS/getting_started/troubleshooting | Troubleshooting page]] | ||
| − | * Post your issue on the forum: https://forum.radxa.com/c/ | + | * Post your issue on the forum: https://forum.radxa.com/c/rockpiS |
Latest revision as of 07:21, 8 December 2023
ROCK Pi S > Getting started
Contents
[hide]- 1 What you need
- 2 Close look of ROCK Pi S
- 3 Features
- 4 Starting the board for the first time
- 5 Next Step
- 6 Troubleshooting
This guide is designed for ROCK Pi S enthusiast. The purpose is to learn about the ROCK Pi S board as well as how to prepare and set up for basic use. We will introduce the board information as much as possible.
What you need
Necessary
- ROCK Pi S main board
- One of the Storage media below:
- μSD card, larger than 8GB.
- USB type C to type A cable
- For both power and USB communication(adb/fastboot) with HOST PC.
- PC/Laptop which has USB ports
- The ROCK Pi S can be powered from the PC/Laptop USB ports directly
Optional
- Power adapter
- If you want to power ROCK Pi S standalone, you can use 5V/1A or 5V/2A power adapter with USB C ports. You can also use the USB PD/QC power adapter without worrying damage the board because the PD/QC adapter will detect ROCK Pi S only supports 5V so the adapter will output 5V.
- μSD Card Reader
- For flashing the image into μSD Card.
- USB to TTL serial cable
- For serial console, low level troubleshooting, development etc.
- Ethernet cable
- ROCK Pi S supports Internet access via WIFI or Ethernet.
- An Ethernet cable is used to connect your ROCK Pi S to a local network and the Internet.
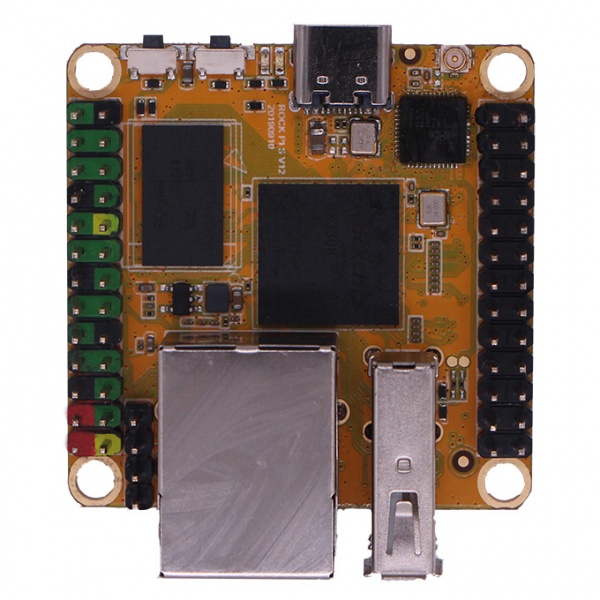
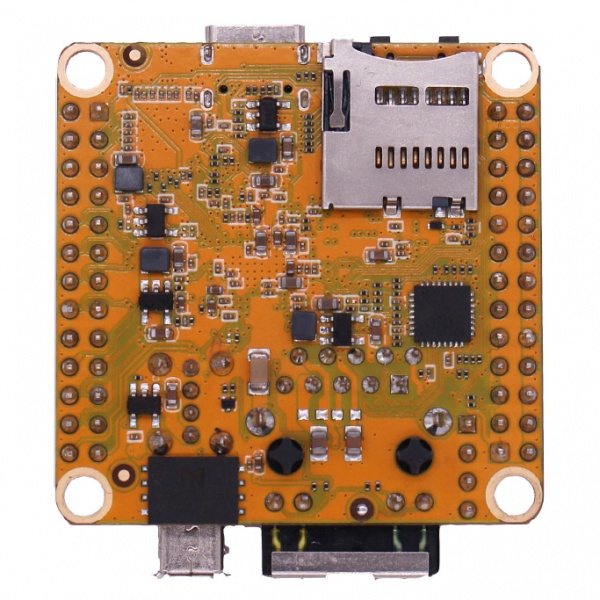
Close look of ROCK Pi S
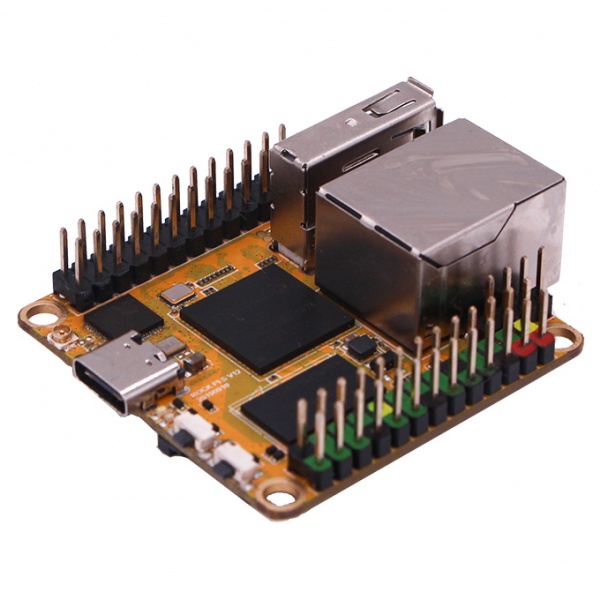
- ROCK Pi S front view
- ROCK Pi S front with an angle view
- ROCK Pi S back view
Features
| Model | ROCK Pi S | |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | SoC RK3308B Quad Cortex-A35 ARM 64bits processor frequency up to 1.0GHz | |
| Memory | 256MB or 512MB DDR3 | |
| Storage | MicroSD(TF), optional on board 1/2/4/8Gb NAND flash | |
| Wireless | 802.11 b/g/n wifi BT 4.0(rtl8723DS) external antenna | |
| USB | USB2.0 Type-A HOST x1 USB3.0 Type-C OTG x1 | |
| Key | maskrom x1 reset x1 | |
| Ethernet | 100MB ethernet, optional PoE(additional HAT requried) | |
| IO | 26-pin expansion header I2C x4 PWM x3 SPI x2 UART x3 I2S0 x1 5V DC power in x2 3.3V DC power in x2 | |
| Others | --- | |
| Power | USB Type-C DC 5V | |
| Size | 1.7inch square | |
Starting the board for the first time
ROCK Pi S can be started with μSD Card.
1. Prepare the image
- When start system with μSD Card
Insert the μSD Card into μSD Card Reader, which connects to host computer.
2. Write Image to uSD card
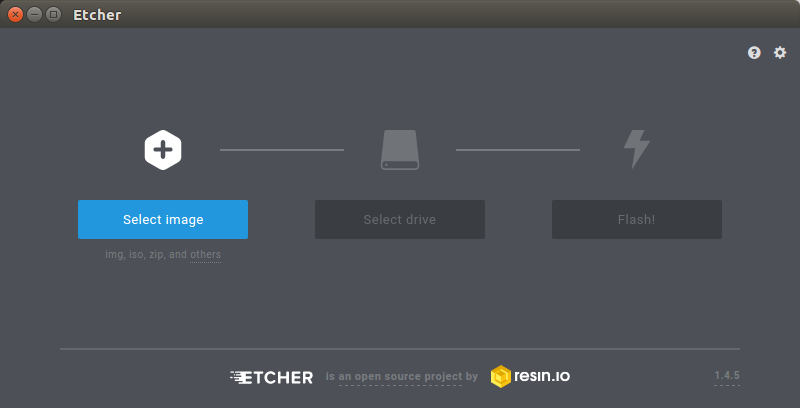
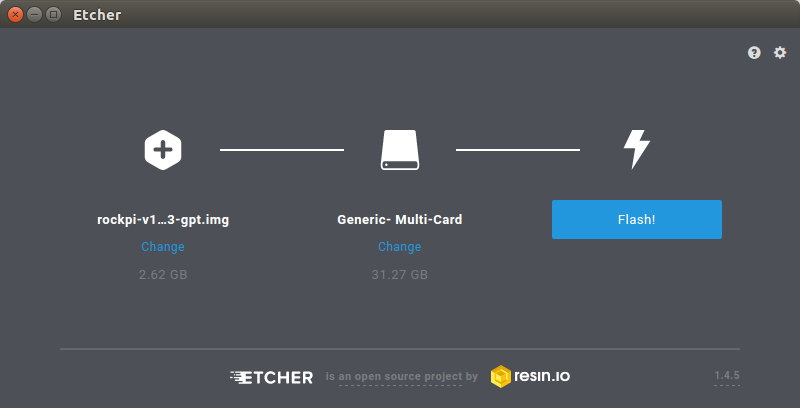
- Download the flash tool, etcher, from Downloads. Choose the right version for your host operation system. Here we operate on host Ubuntu 16.04.
- After unpacking the package, we run the tool by executing the command
$ ./etcher-etcher-electron-1.4.5-x86_64.AppImage
If you get an error message: "No polkit authentication agent found" you can try and start it with sudo, but do know that this is running the tool as root.
- In the etcher window, click Select image.
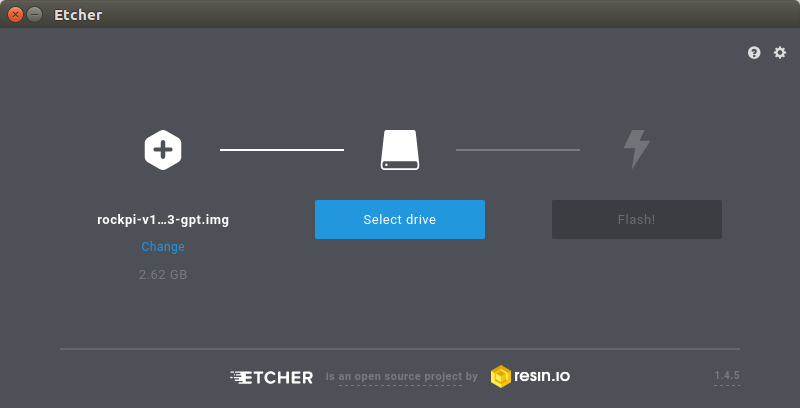
- In the etcher window, click Select Drive.
- In the etcher window, click Flash.
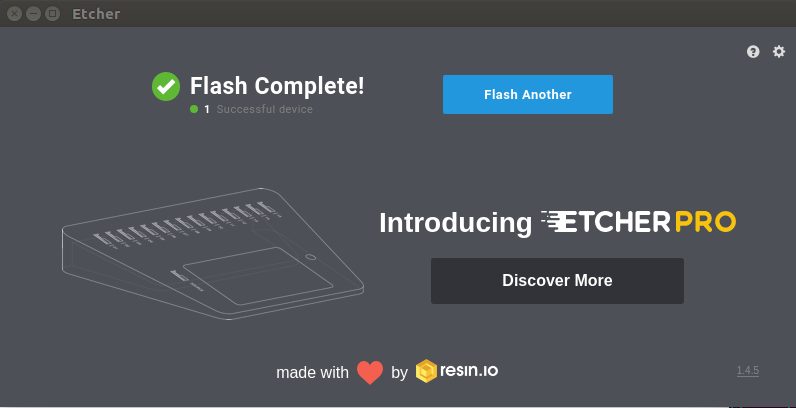
- In the etcher window, once it shows us Flash Complete! It is done and can be put into the ROCK Pi S.
3. Boot the board
- Now insert the uSD card to the board.
- Use a USB C to USB A cable, connect the board to your PC
- ROCK Pi S will boot, the green power led is on, and after a while, the blue led start blinking
- (Optional)Use a USB to TTL serial cable to make a connection between your PC and ROCK Pi S. See Serial Console
4. Access from the Host PC/Laptop
Option 1: USB access(adb)
By default, the ROCK Pi S Linux image enables adbd services, which is a debug bridge from Android now ported on Linux. With one USB A to C cable you can power and access the board, very handy.
To use adb, you need to install adb tool on the PC/Laptop. Check instructions for Windows and Linux.
After you have adb installed successfully, run the following command on console to login the shell of ROCK Pi S:
adb shell
Check Using adb.
Option 2: Serial console
Check Serial Console
Option 3: SSH
SSH server is enabled on port 22 of ROCK Pi S default image.
Please use angryip to find your board IP address.
To access ROCK Pi S by SSH, try
ping rockpis.local ssh rock@rockpis.local
or if your router/network doesn't support Local Domain, you need to check your network/router administrator page and look for the ROCK Pi S ip address.
ping ip-of-device ssh rock@ip-of-device
Note: You can also get the IP of ROCK Pi S from option 1 or option 2 if you can not access network administrator page.
5.Network state
- Look at network configure:
$ sudo ifconfig
- Test network:
$ ping -c 5 www.google.com
6.WIFI Connection
Check WIFI Connection.
7.BT
Check BT.
8.Buttons
ROCK Pi S has reset key and maskrom key:
- Reset key:
Press and release this key to reset ROCK Pi S.
- Maskrom key:
ROCK Pi S supports boot on SD NAND flash. By default, SD NAND starts before TF card. Press the maskrom key to ignore the SD NAND flash when ROCK Pi S is powered on.
9.LED
ROCK Pi S has Power LED and User LED.
- Power LED
Power LED is green, which can be configured by sysfs.
The related directory is /sys/class/leds/rockpis:green:power
It is always on when ROCK Pi S is given power by default,
- User LED
User LED is blue, which can be configured by sysfs.
The related directory is /sys/class/leds/rockpis:blue:user
By default, its blink status shows the running kernel.
10.GPIO
ROCK Pi S has two 26-pin expansion headers. Each pin is distinguished by color, more information click here
Development for GPIO ROCK Pi S support libmraa GPIO library, click here to get more information.
11.Using OTG
ROCK Pi S has an USB type-C OTG connector, which you can use to write(or read) data by PC to (or from) ROCK Pi S, more help click here
Next Step
- More Debian image usage and tips
- Install image to SD Nand if your board has
- Checkout the hardware details
- Join the community and the discussion group
Troubleshooting
- Refer Troubleshooting page
- Post your issue on the forum: https://forum.radxa.com/c/rockpiS