Difference between revisions of "Zero"
RadxaYuntian (Talk | contribs) (Update language and add description on some items. Android section is removed since there is currently nothing written for it.) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
This is the Wiki page for Radxa Zero, written by Radxa Team with community contributions. | This is the Wiki page for Radxa Zero, written by Radxa Team with community contributions. | ||
| − | Radxa Zero is an ultra thin SBC in small form factor with powerful performance based on Amlogic S905Y2. It can run | + | Radxa Zero is an ultra thin SBC in small form factor with powerful performance based on Amlogic S905Y2. It can run Android and selected Linux distributions. |
| − | Radxa Zero features a quad core 64 ARM processor, 32bit LPDDR4, | + | Radxa Zero features a quad core 64-bit ARM processor, up to 4GB 32bit LPDDR4 memory, HDMI output at 4K@60, WiFi 5, Bluetooth 5.0, USB 3.0, and 40-pin GPIO header. Additionally, the power port can also be used for USB 2.0 OTG to connect more peripheral. |
| − | Radxa Zero comes in | + | Radxa Zero comes in multiple configurations to suit your need. Please check [[zero/hardware/models | Models & SKU]] for detail. |
</div> <!-- col-md-8 --> | </div> <!-- col-md-8 --> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
<div class="panel-body"> | <div class="panel-body"> | ||
| − | Installing an operating system on your Zero | + | Installing an operating system on your Zero. Booting from [[Zero/getting_started#Write_Image | micro SD]] or eMMC module are supported. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* [[zero/install/eMMC_erase | Erase eMMC]] | * [[zero/install/eMMC_erase | Erase eMMC]] | ||
| − | + | * [[zero/install/eMMC | Install Linux to eMMC]] | |
| + | * [[zero/install/eMMC_Android9 | Install Android 9 to eMMC]] | ||
</div> <!-- panel-body --> | </div> <!-- panel-body --> | ||
</div> <!-- panel panel-mango-white --> | </div> <!-- panel panel-mango-white --> | ||
</div> <!-- col-md-4 --> | </div> <!-- col-md-4 --> | ||
| + | |||
<div class="col-md-4"> | <div class="col-md-4"> | ||
<div class="panel panel-mango-white"> | <div class="panel panel-mango-white"> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
<div class="panel-body"> | <div class="panel-body"> | ||
| − | * [[zero/dev/serial-console | | + | * [[zero/dev/serial-console | Attach to serial console]] |
| − | * [[zero/dev/u-boot | Build | + | * [[zero/dev/adb | Connect with ADB]] |
| + | * [[zero/dev/usb-mass-storage | Enable USB Mass Storage mode]] | ||
| + | * [[zero/dev/u-boot | Build U-Boot]] | ||
* [[zero/dev/kernel| Build kernel]] | * [[zero/dev/kernel| Build kernel]] | ||
| − | + | * [[zero/dev/libmraa | Install Libmraa]] to enable GPIO access and more | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * [[zero/dev/libmraa | Install Libmraa]] | + | |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
<div class="panel-body"> | <div class="panel-body"> | ||
| − | Technical specifications about the Radxa Zero hardware, including components datasheet, etc. | + | Technical specifications about the Radxa Zero hardware, including components datasheet, schematic, etc. |
* [[zero/hardware/zero | Main board]] - Hardware introduction of the Radxa Zero | * [[zero/hardware/zero | Main board]] - Hardware introduction of the Radxa Zero | ||
| − | + | * [https://dl.radxa.com/zero/docs/hw/S905Y2%20Quick%20Reference%20Manual%20v0.7.pdf S905Y2 Quick Reference Manual] - The SoC datasheet of Radxa Zero | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
* [[zero/hardware/models | Models and SKU]] | * [[zero/hardware/models | Models and SKU]] | ||
| − | |||
* [[zero/hardware/display | Display]] | * [[zero/hardware/display | Display]] | ||
* [[zero/hardware/camera/ | Camera module]] | * [[zero/hardware/camera/ | Camera module]] | ||
| + | * [[Device-tree-overlays | Device Tree Overlays]] | ||
[[zero/hardware | > More...]] | [[zero/hardware | > More...]] | ||
| Line 111: | Line 104: | ||
<div class="panel-heading"><h3 class="panel-title"><i class="fa fa-linux"></i> [[zero/Linux | Working With Linux ]]</h3></div> | <div class="panel-heading"><h3 class="panel-title"><i class="fa fa-linux"></i> [[zero/Linux | Working With Linux ]]</h3></div> | ||
<div class="panel-body"> | <div class="panel-body"> | ||
| − | Fundamental Linux usage for beginners and | + | Fundamental Linux usage for beginners and advanced use cases for power users. |
* [[zero/Debian | Debian]] | * [[zero/Debian | Debian]] | ||
* [[zero/Ubuntu | Ubuntu]] | * [[zero/Ubuntu | Ubuntu]] | ||
| − | * [[zero/radxa-apt | Radxa APT]] | + | * [[zero/radxa-apt | Radxa APT repository]] |
| − | * [[zero/downloads | | + | * [[zero/downloads | Download images]] |
</div> <!-- panel-body --> | </div> <!-- panel-body --> | ||
</div> <!-- panel panel-mango-white --> | </div> <!-- panel panel-mango-white --> | ||
</div> <!-- col-md-4 --> | </div> <!-- col-md-4 --> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 07:03, 1 December 2021
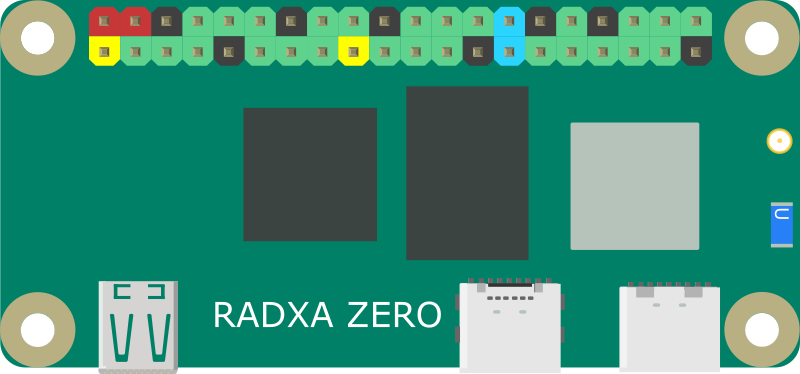
Radxa Zero
This is the Wiki page for Radxa Zero, written by Radxa Team with community contributions.
Radxa Zero is an ultra thin SBC in small form factor with powerful performance based on Amlogic S905Y2. It can run Android and selected Linux distributions.
Radxa Zero features a quad core 64-bit ARM processor, up to 4GB 32bit LPDDR4 memory, HDMI output at 4K@60, WiFi 5, Bluetooth 5.0, USB 3.0, and 40-pin GPIO header. Additionally, the power port can also be used for USB 2.0 OTG to connect more peripheral.
Radxa Zero comes in multiple configurations to suit your need. Please check Models & SKU for detail.
- 2022-07-08: OpenSUSE now supports Radxa Zero, installation tutorials from OpenSUSE Wiki.
- 2022-06-23: ROCK 5B Developer Edition is shipping, checkout the Debug Party
- 2022-01-09: ROCK 5 Model B is announced: an ARM64 desktop level SBC
- 2021-10-11: Radxa Zero Debian/Ubuntu system images are released. Check the Radxa Zero Downloads.
- 2021-08-25: ROCK 3A Debian/Ubuntu system images are released. Check the ROCK 3 Downloads.
- 2021-07-11: IOhub is even more affordable with ROCK PI X hardware
- 2021-06-16: Radxa Zero is released
- 2021-04-15: ROCK PI S Based GPS NTP appliance is launched
- 2021-03-13: Build a Mini Serene Screen Aquarium with ROCK Pi X
- 2021-03-11: ROCK Pi 4 as the perfect Chia coin crypto currency farmer
- Getting started with your Radxa Zero, including what you need and how to get it booted.
- GPIO pinout
Installing an operating system on your Zero. Booting from micro SD or eMMC module are supported.
- Attach to serial console
- Connect with ADB
- Enable USB Mass Storage mode
- Build U-Boot
- Build kernel
- Install Libmraa to enable GPIO access and more
Technical specifications about the Radxa Zero hardware, including components datasheet, schematic, etc.
- Main board - Hardware introduction of the Radxa Zero
- S905Y2 Quick Reference Manual - The SoC datasheet of Radxa Zero
- Models and SKU
- Display
- Camera module
- Device Tree Overlays