Difference between revisions of "Zero/install/eMMC"
RadxaYuntian (Talk | contribs) |
RadxaYuntian (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{zero_header}} | {{zero_header}} | ||
| + | |||
{{Languages|zero/install/eMMC}} | {{Languages|zero/install/eMMC}} | ||
| + | |||
[[zero | Radxa Zero]] > [[zero/install | Installation]] > [[zero/install/eMMC | Install image to eMMC]] | [[zero | Radxa Zero]] > [[zero/install | Installation]] > [[zero/install/eMMC | Install image to eMMC]] | ||
| − | === How to install | + | === How to install Linux image to Radxa Zero eMMC === |
| − | This guide describes how to install the raw images to Radxa Zero eMMC. Raw | + | This guide describes how to install the raw images to Radxa Zero series eMMC. Raw image is the standard method to install Linux distro on single board computers, since they don't have standardized way to boot and initialize their hardware. |
== Requirement == | == Requirement == | ||
| − | * Radxa Zero | + | * Radxa Zero or Radxa Zero 2 |
* A PC/laptop running Windows, Linux, or macOS | * A PC/laptop running Windows, Linux, or macOS | ||
* USB A to C cable or C to C cable, depending on your host | * USB A to C cable or C to C cable, depending on your host | ||
| − | * A supported Linux image | + | * A supported Linux image |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == Windows == | + | == Install using Windows == |
| − | + | If you have existing data that you want to keep, this is your last chance to do so. Please follow [[Zero/dev/maskrom#Enable_maskrom | maskrom guide]] to load <code>rz-udisk-loader.bin</code> and make backup accordingly. | |
| − | + | Now follow [[Zero/install/eMMC_erase | eMMC erase guide]] to wipe out the existing system. Your computer should detect a new storage device after the file is loaded. | |
| − | + | You can now flash your Linux image using balenaEtcher similar to [[Zero/getting_started#Write_Image | flash microSD card]]. Choose the newly detected device in your target drive and proceed as normal. | |
| − | + | Once you are done flashing, unplug and replug Radxa Zero to quit maskrom mode and boot normally. | |
| − | + | == Install using Linux or macOS == | |
| − | + | If you have existing data that you want to keep, this is your last chance to do so. Please follow [[Zero/dev/maskrom#Enable_maskrom | maskrom guide]] to load <code>rz-udisk-loader.bin</code> and make backup accordingly. | |
| − | + | Now follow [[Zero/install/eMMC_erase | eMMC erase guide]] to wipe out the existing system. Your computer should detect a new storage device after the file is loaded. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Now lsusb should show the following device: | Now lsusb should show the following device: | ||
| − | Bus 001 Device | + | Bus 001 Device 049: ID 1b8e:2200 Amlogic, Inc. USB download gadget |
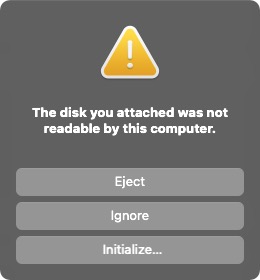
The Zero is in USB disk mode now, your computer should popup a new USB drive. On macOS you will get a disk not readable popup. Just click Ignore: | The Zero is in USB disk mode now, your computer should popup a new USB drive. On macOS you will get a disk not readable popup. Just click Ignore: | ||
| Line 126: | Line 73: | ||
sync | sync | ||
| − | + | Once you are done flashing, unplug and replug Radxa Zero to quit maskrom mode and boot normally. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 02:49, 23 January 2022
Radxa Zero > Installation > Install image to eMMC
Contents
How to install Linux image to Radxa Zero eMMC
This guide describes how to install the raw images to Radxa Zero series eMMC. Raw image is the standard method to install Linux distro on single board computers, since they don't have standardized way to boot and initialize their hardware.
Requirement
- Radxa Zero or Radxa Zero 2
- A PC/laptop running Windows, Linux, or macOS
- USB A to C cable or C to C cable, depending on your host
- A supported Linux image
Install using Windows
If you have existing data that you want to keep, this is your last chance to do so. Please follow maskrom guide to load rz-udisk-loader.bin and make backup accordingly.
Now follow eMMC erase guide to wipe out the existing system. Your computer should detect a new storage device after the file is loaded.
You can now flash your Linux image using balenaEtcher similar to flash microSD card. Choose the newly detected device in your target drive and proceed as normal.
Once you are done flashing, unplug and replug Radxa Zero to quit maskrom mode and boot normally.
Install using Linux or macOS
If you have existing data that you want to keep, this is your last chance to do so. Please follow maskrom guide to load rz-udisk-loader.bin and make backup accordingly.
Now follow eMMC erase guide to wipe out the existing system. Your computer should detect a new storage device after the file is loaded.
Now lsusb should show the following device:
Bus 001 Device 049: ID 1b8e:2200 Amlogic, Inc. USB download gadget
The Zero is in USB disk mode now, your computer should popup a new USB drive. On macOS you will get a disk not readable popup. Just click Ignore:
On Linux you will get following output from sudo dmesg:
[74292.229573] usb 1-10.2.3: new high-speed USB device number 84 using xhci_hcd [74292.330483] usb 1-10.2.3: New USB device found, idVendor=1b8e, idProduct=c003, bcdDevice= 0.20 [74292.330487] usb 1-10.2.3: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=0 [74292.330488] usb 1-10.2.3: Product: GX-CHIP [74292.330489] usb 1-10.2.3: Manufacturer: Amlogic [74303.432510] usb 1-10.2.3: USB disconnect, device number 84 [74303.665204] usb 1-10.2.3: new high-speed USB device number 85 using xhci_hcd [74303.769674] usb 1-10.2.3: New USB device found, idVendor=1b8e, idProduct=2200, bcdDevice=99.99 [74303.769678] usb 1-10.2.3: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 [74303.769679] usb 1-10.2.3: Product: USB download gadget [74303.769680] usb 1-10.2.3: Manufacturer: Radxa [74303.769681] usb 1-10.2.3: SerialNumber: AMLG12A-RADXA-ZERO [74303.771008] usb-storage 1-10.2.3:1.0: USB Mass Storage device detected [74303.771133] scsi host4: usb-storage 1-10.2.3:1.0 [74304.785353] scsi 4:0:0:0: Direct-Access Linux Radxa Zero UDisk 0ff PQ: 0 ANSI: 2 [74304.785506] sd 4:0:0:0: Attached scsi generic sg2 type 0 [74304.785679] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] 60749504 512-byte logical blocks: (31.1 GB/29.0 GiB) [74304.785796] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] Write Protect is off [74304.785798] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] Mode Sense: 0f 00 00 00 [74304.785916] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] Write cache: enabled, read cache: enabled, doesn't support DPO or FUA [74304.833523] sdc: sdc1 [74304.861751] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] Attached SCSI removable disk [74305.424709] EXT4-fs (sdc1): recovery complete [74305.425517] EXT4-fs (sdc1): mounted filesystem with writeback data mode. Opts: (null). Quota mode: none.
You can now use dd to write the raw image to the eMMC on Zero now.
sudo dd if=/path/to/image of=/dev/new_dev bs=1M sync
Once you are done flashing, unplug and replug Radxa Zero to quit maskrom mode and boot normally.