Difference between revisions of "AI/RKNN-Toolkit"
(→Example) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Languages|AI/RKNN-Toolkit}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Home | Home]] > [[AI | AI Development]] > [[AI/RKNN-Toolkit | RKNN Toolkit]] | ||
| + | |||
=== Introduction === | === Introduction === | ||
| Line 11: | Line 15: | ||
3) '''performance evaluation''': user can simulate running the model on a PC to get both the total time spent on the model and the time-consuming information of each layer. User can also run the model on the specified hardware platform RK3399Pro/RK1808 by online debugging, and get both the total time of the model running on the hardware and the time-consuming information of each layer. | 3) '''performance evaluation''': user can simulate running the model on a PC to get both the total time spent on the model and the time-consuming information of each layer. User can also run the model on the specified hardware platform RK3399Pro/RK1808 by online debugging, and get both the total time of the model running on the hardware and the time-consuming information of each layer. | ||
| − | This chapter mainly explains how to perform model conversion on the RK3399Pro/RK1808 development board. For other function descriptions, please refer to the | + | This chapter mainly explains how to perform model conversion on the RK3399Pro/RK1808 development board. For other function descriptions, please refer to the [https://dl.radxa.com/rockpin10/docs/sw/rknn-toolkit/Rockchip_User_Guide_RKNN_Toolkit_V1.3.0_EN.pdf RKNN-Toolkit User Guide]. |
=== Installation preparation === | === Installation preparation === | ||
| Line 40: | Line 44: | ||
==== Example ==== | ==== Example ==== | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python" line='line'> | |
| − | + | from rknn.api import RKNN | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | INPUT_SIZE = 64 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if __name__ == '__main__': | |
| − | + | rknn = RKNN() # Create an RKNN execution object | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ''' | |
| − | + | Configure model input for NPU preprocessing of input data | |
| − | + | channel_mean_value='0 0 0 255', when runing forward inference, the RGB data will be | |
| − | + | converted as follows (R - 0) / 255, (G - 0) / 255, (B - 0) / 255, | |
| − | + | The RKNN model automatically performs the mean and normalization. | |
| − | + | reorder_channel='0 1 2' , used to specify whether to adjust the image channel order, | |
| − | + | set to 0 1 2, means no adjustment according to the input image channel order. | |
| + | reorder_channel='2 1 0' , indicates that 0 and 2 channels are exchanged. | ||
| + | If the input is RGB, it will be adjusted to BGR. If it is BGR will be adjusted to RGB | ||
| + | Image channel order is not adjusted | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | rknn.config(channel_mean_value='0 0 0 255', reorder_channel='0 1 2') | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | load TensorFlow model | ||
| + | tf_pb='digital_gesture.pb' specify the TensorFlow model to be converted | ||
| + | inputs specify the input node in the model | ||
| + | outputs specify the output node in the model | ||
| + | input_size_list specify the size of the model input | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | print('--> Loading model') | ||
| + | rknn.load_tensorflow(tf_pb='digital_gesture.pb', | ||
| + | inputs=['input_x'], | ||
| + | outputs=['probability'], | ||
| + | input_size_list=[[INPUT_SIZE, INPUT_SIZE, 3]]) | ||
| + | print('done') | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | Create a parsing pb model | ||
| + | do_quantization=False do not to be quantified | ||
| + | Quantization will reduce the size of the model and increase the speed of the operation, | ||
| + | but there will be loss of precision. | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | print('--> Building model') | ||
| + | rknn.build(do_quantization=False) | ||
| + | print('done') | ||
| + | rknn.export_rknn('./digital_gesture.rknn') # Export and save rknn model file | ||
| + | rknn.release() # Release RKNN Context | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== Model Inference === | === Model Inference === | ||
| Line 93: | Line 103: | ||
==== Example ==== | ==== Example ==== | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python" line='line'> | |
| − | + | import numpy as np | |
| − | + | from PIL import Image | |
| − | + | from rknn.api import RKNN | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Analyze the output of the model to get the most probable gesture and corresponding probability | |
| − | + | def get_predict(probability): | |
| − | + | data = probability[0][0] | |
| − | + | data = data.tolist() | |
| − | + | max_prob = max(data) | |
| − | + | return data.index(max_prob), max_prob | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | def load_model(): | |
| − | + | rknn = RKNN() # Create an RKNN execution object | |
| − | + | print('-->loading model') | |
| − | + | rknn.load_rknn('./digital_gesture.rknn') # Load RKNN model | |
| − | + | print('loading model done') | |
| − | + | print('--> Init runtime environment') | |
| − | + | ret = rknn.init_runtime(host='rk3399pro') # Initialize the RKNN runtime environment | |
| − | + | if ret != 0: | |
| − | + | print('Init runtime environment failed') | |
| − | + | exit(ret) | |
| − | + | print('done') | |
| − | + | return rknn | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | def predict(rknn): | |
| − | + | im = Image.open("../picture/6_7.jpg") # load image | |
| − | + | im = im.resize((64, 64), Image.ANTIALIAS) # Image resize to 64x64 | |
| − | + | mat = np.asarray(im.convert('RGB')) # Convert to RGB format | |
| − | + | outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[mat]) # Run forward inference and get the inference result | |
| − | + | pred, prob = get_predict(outputs) # Transform the inference results into visual information | |
| − | + | print(prob) | |
| − | + | print(pred) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if __name__=="__main__": | |
| − | + | rknn = load_model() | |
| − | + | predict(rknn) | |
| + | rknn.release() | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:30, 16 March 2020
Home > AI Development > RKNN Toolkit
Contents
Introduction
Rockchip offers the RKNN-Toolkit development kit for model conversion, forward inference, and performance evaluation.
Users can easily perform the following functions through the provided Python interface:
1) Model conversion: support Caffe、Tensorflow、TensorFlow Lite、ONNX、Darknet model, support RKNN model import and export, and so the models can be loaded and used on the hardware platform.
2) forward inference: user can simulate running the model on the PC and get the inference results, and run the model on the specified hardware platform RK3399Pro/RK1808 and get the inference results.
3) performance evaluation: user can simulate running the model on a PC to get both the total time spent on the model and the time-consuming information of each layer. User can also run the model on the specified hardware platform RK3399Pro/RK1808 by online debugging, and get both the total time of the model running on the hardware and the time-consuming information of each layer.
This chapter mainly explains how to perform model conversion on the RK3399Pro/RK1808 development board. For other function descriptions, please refer to the RKNN-Toolkit User Guide.
Installation preparation
sudo dnf install -y cmake gcc gcc-c++ protobuf-devel protobuf-compiler lapack-devel sudo dnf install -y python3-devel python3-opencv python3-numpy-f2py python3-h5py python3-lmdb python3-grpcio pip3 install scipy-1.2.0-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl pip3 install onnx-1.4.1-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl pip3 install tensorflow-1.10.1-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl
After installing the above basic package, install the rknn-toolkit wheel package. RKNN wheel package and other Python wheel packages can be downloaded from OneDrive.
Since pip does not have a ready-made aarch64 version of the scipy and onnx wheel packages, we have provided a compiled wheel package. If you want the latest version of the wheel package or find a problem with the pre-compiled wheel package, you can use pip to install it yourself. This will compile and install the wheel package. It will take a long time and you need to wait patiently.
pip3 install scipy pip3 install onnx
If the installation encounters an error, please install the corresponding software package according to the error message.
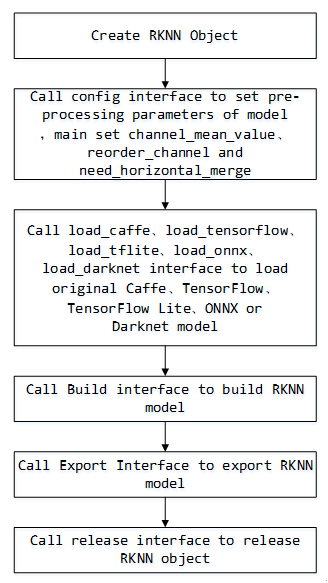
Model Conversion
API call flow
Example
from rknn.api import RKNN
INPUT_SIZE = 64
if __name__ == '__main__':
rknn = RKNN() # Create an RKNN execution object
'''Configure model input for NPU preprocessing of input datachannel_mean_value='0 0 0 255', when runing forward inference, the RGB data will beconverted as follows (R - 0) / 255, (G - 0) / 255, (B - 0) / 255,The RKNN model automatically performs the mean and normalization.reorder_channel='0 1 2' , used to specify whether to adjust the image channel order,set to 0 1 2, means no adjustment according to the input image channel order.reorder_channel='2 1 0' , indicates that 0 and 2 channels are exchanged.If the input is RGB, it will be adjusted to BGR. If it is BGR will be adjusted to RGBImage channel order is not adjusted'''rknn.config(channel_mean_value='0 0 0 255', reorder_channel='0 1 2')
'''load TensorFlow modeltf_pb='digital_gesture.pb' specify the TensorFlow model to be convertedinputs specify the input node in the modeloutputs specify the output node in the modelinput_size_list specify the size of the model input'''print('--> Loading model')
rknn.load_tensorflow(tf_pb='digital_gesture.pb',
inputs=['input_x'],
outputs=['probability'],
input_size_list=[[INPUT_SIZE, INPUT_SIZE, 3]])
print('done')
'''Create a parsing pb modeldo_quantization=False do not to be quantifiedQuantization will reduce the size of the model and increase the speed of the operation,but there will be loss of precision.'''print('--> Building model')
rknn.build(do_quantization=False)
print('done')
rknn.export_rknn('./digital_gesture.rknn') # Export and save rknn model file
rknn.release() # Release RKNN Context
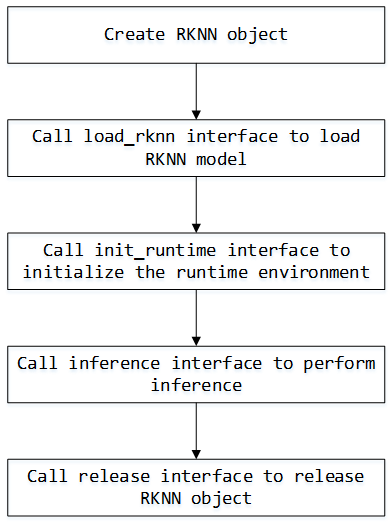
Model Inference
API call flow
Example
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from rknn.api import RKNN
# Analyze the output of the model to get the most probable gesture and corresponding probabilitydef get_predict(probability):
data = probability[0][0]
data = data.tolist()
max_prob = max(data)
return data.index(max_prob), max_prob
def load_model():
rknn = RKNN() # Create an RKNN execution object
print('-->loading model')
rknn.load_rknn('./digital_gesture.rknn') # Load RKNN model
print('loading model done')
print('--> Init runtime environment')
ret = rknn.init_runtime(host='rk3399pro') # Initialize the RKNN runtime environment
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
return rknndef predict(rknn):
im = Image.open("../picture/6_7.jpg") # load image
im = im.resize((64, 64), Image.ANTIALIAS) # Image resize to 64x64
mat = np.asarray(im.convert('RGB')) # Convert to RGB format
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[mat]) # Run forward inference and get the inference result
pred, prob = get_predict(outputs) # Transform the inference results into visual information
print(prob)
print(pred)
if __name__=="__main__":
rknn = load_model()
predict(rknn)
rknn.release()