Difference between revisions of "Rock5/install/eMMC"
m (Language Header correction) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{rock5_header}} | {{rock5_header}} | ||
| − | {{Languages|rock5/install/ | + | {{Languages|rock5/install/eMMC}} |
[[rock5 | ROCK 5]] > [[rock5/install | Installation]] > [[rock5/install/eMMC | Install the image to eMMC with USB to eMMC Reader]] | [[rock5 | ROCK 5]] > [[rock5/install | Installation]] > [[rock5/install/eMMC | Install the image to eMMC with USB to eMMC Reader]] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* ROCK 5B | * ROCK 5B | ||
| − | === | + | === Option 1: Write one system image to eMMC module === |
In part one let's focus on writing one system image to eMMC module. Here we test it with ROCK 5B board. | In part one let's focus on writing one system image to eMMC module. Here we test it with ROCK 5B board. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
Done! Now you have successfully installed the OS image on eMMC module. | Done! Now you have successfully installed the OS image on eMMC module. | ||
| − | === | + | === Option 2: Erase eMMC module === |
When eMMC module is written with Android (or Linux) images before, now we change to Linux( or Android). It's recommended that you erase eMMC module first. Then write the target images. | When eMMC module is written with Android (or Linux) images before, now we change to Linux( or Android). It's recommended that you erase eMMC module first. Then write the target images. | ||
| − | === | + | === Option 3: Write bootloader only to eMMC module === |
In part three let's take a look know to write U-Boot images to eMMC module. | In part three let's take a look know to write U-Boot images to eMMC module. | ||
Latest revision as of 21:57, 9 September 2023
ROCK 5 > Installation > Install the image to eMMC with USB to eMMC Reader
Install the image to eMMC module with USB to eMMC Reader
This guide describes how to write images to eMMC module and erase eMMC module for ROCK 5 serial boards.
Available ROCK 5 boards:
- ROCK 5B
Option 1: Write one system image to eMMC module
In part one let's focus on writing one system image to eMMC module. Here we test it with ROCK 5B board.
Step one: Requirements
- ROCK 5B board with power supply
- one eMMC module, larger than 8GB
- one USB to eMMC reader
- one PC/laptop running Windows or Linux or MacOS
Step two: Download necessary tools and image
- Etcher is the tool we use to write image. Download the right Etcher for your PC from ROCK 5 Downloads page and install it. Check Etcher website for more info about Etcher.
- Choose the image you want to install from ROCK 5 Downloads page.
Here we use the following image for writing.
rock-5b-debian-bullseye-xfce4-arm64-20220420-0439-gpt.img.xz
Step three: Write the image to eMMC module
- Insert the eMMC module into USB to eMMC reader, which connects to host computer.
- Run the application. For example double click balenaEtcher-1.7.9-x64.AppImage on Ubuntu 20.04:
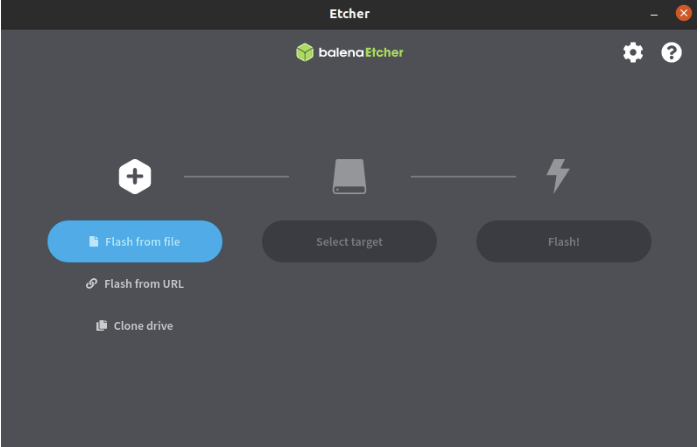
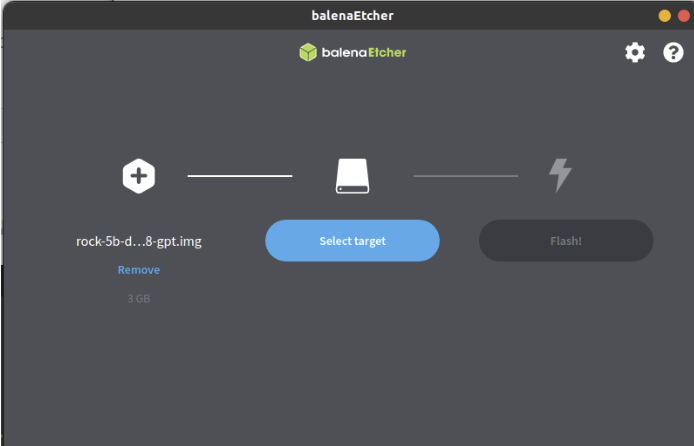
- In the etcher window, we click button Select image.
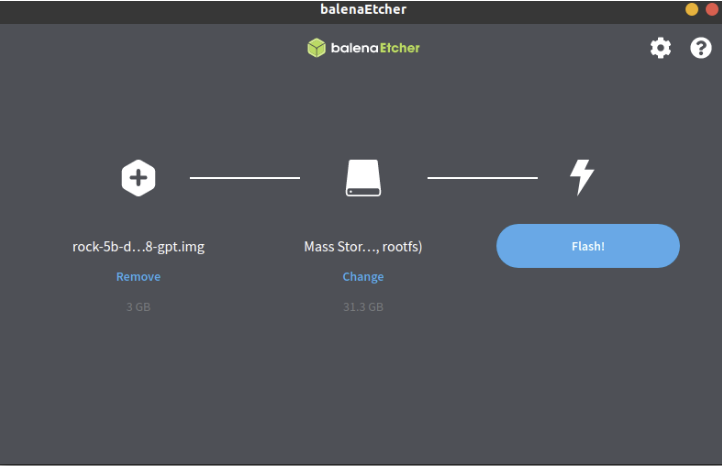
- In the etcher window, we click button Select Drive.
- In the etcher window, we click button Flash.
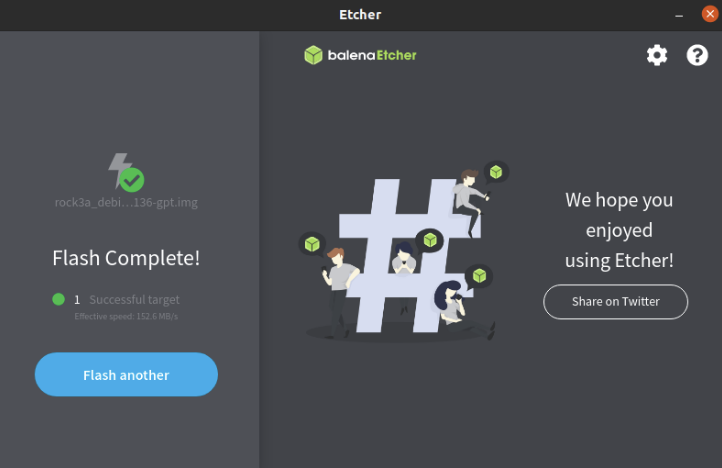
- In the etcher window, it shows us Flash Complete!
Done! Now you have successfully installed the OS image on eMMC module.
Option 2: Erase eMMC module
When eMMC module is written with Android (or Linux) images before, now we change to Linux( or Android). It's recommended that you erase eMMC module first. Then write the target images.
Option 3: Write bootloader only to eMMC module
In part three let's take a look know to write U-Boot images to eMMC module. We have prebuilt u-boot images built via rockchip-bsp SDK. They're idbloader.img and u-boot.itb.
On Linux PC:
$ sudo dd if=./idbloader.img of=/dev/sdX seek=64 $ sudo dd if=./u-boot.itb of=/dev/sdX seek=16384
On Mac PC:
% sudo dd if=./idbloader.img of=/dev/diskX seek=64 % sudo dd if=./u-boot.itb of=/dev/diskX seek=16384